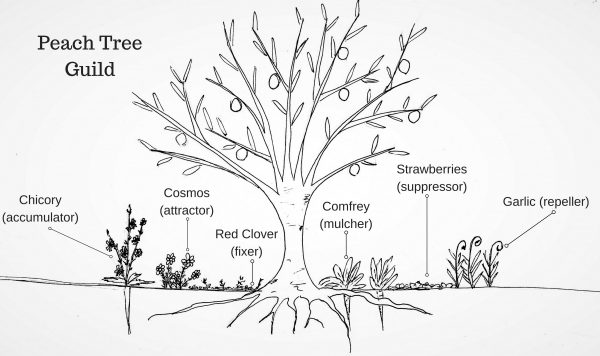
For those who aren’t familiar a fruit tree guild is a permaculture method of planting a fruit tree in combination with other plants that will grow together to create a mini ecosystem around the tree. While there hasn’t been a lot of scientific study of tree guilds they do show a lot of potential. Research has shown that intercropping (planting more than one species together) can be a valuable tool for increasing yields and crop health. Plus, tree guilds, in stark contrast with monoculture orchards are space saving and great for wildlife.
Selecting Plants
The first step is to research the type of tree you’d like to start with. For an example I’ll be talking about a peach tree guild but you can use any type of tree whether it’s an existing tree on your property or one you’d like to plant this spring. The important part is that you do some research into the tree such as its growth pattern and mature size. Also consider what soil types it prefers, where you’ll be planting it, and if it’s prone to any disease or pest problems.
Based on your research you’ll select companion plants. Tree guilds are typically made up of six categories: suppressors, attractors, repellers, mulchers, accumulators, and fixers though there are variations and there’s no rule that you have to plant all of these or can’t plant more than one species from each category. If you see a need you can even make up your own category!
If you’re planting a particularly tall tree or working with a mature tree you can include perennial shrubs on your plant list. Just be careful with smaller, newer trees that they don’t compete for light.
Suppressors
These are plants that suppress weed growth through there own growth habits. Good examples include vining winter squash which shades out weeds, mint or buckwheat which outcompete weeds through rapid, thick growth, or strawberries, pennyroyal, or thyme whose vines form a thick mat of ground cover. For a peach tree guild I would choose strawberries partially because I enjoy eating them but also because they’re an excellent suppressor and their early flowers draw in pollinators.
Attractors
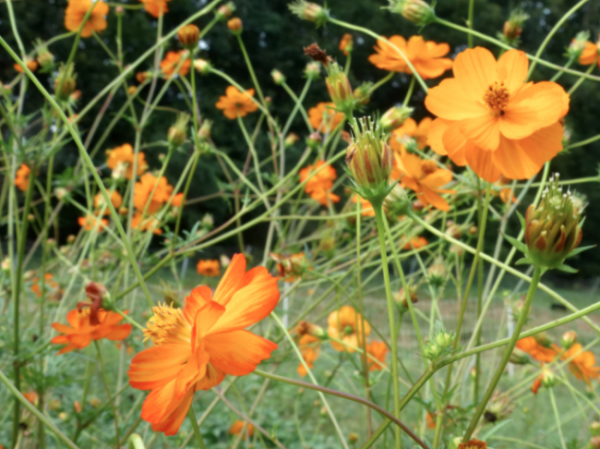

Attractors are plants that attract pollinators and other beneficial insect to the tree. Examples include yarrow, buckwheat, butterfly weed, and mustards. Many other species can also be used but it’s important to find something that will work well for your chosen tree. For a peach tree guild I would choose to plant cosmos as they attract trichogramma wasps which are a helpful beneficial insect and a natural enemy of oriental fruit moths which can severely damage peach trees.
Repellers
These plants job is to repel unwanted pests from feeding on your fruit tree. Lemon grass, marigolds, lemon balm, and almost any allium like garlic, chives, or perennial onions are all commonly used to repel pests. Knowing your specific tree’s common pest issues will allow you to best select a variety. For the peach tree example I’d use garlic as there’s some evidence that planting garlic around peach trees helps repel peach tree borers.
Fixers
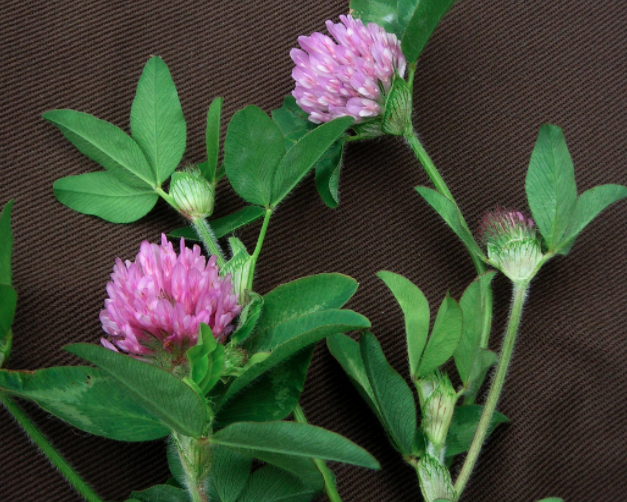

Fixers refers to plants that are nitrogen fixing meaning that they add nitrogen to the soil as they grow. Great examples of these plants include white clover, red clover, beans, alfalfa, lupine, and peas. For a peach tree guild I would choose red clover. It attracts pollinators, beneficial insects including trichogramma wasps, and makes a wonderful tea.
Mulchers
Probably the most commonly used mulcher plant in permaculture designs is comfrey. It’s hardy, perennial, easy to care for, and its leaves do in fact make excellent mulch. Hostas have the same benefits. You can also use annual cover crops like buckwheat that winter kill and provide good mulch. Buckwheat also has the added benefit of self seeding. For this example comfrey will be used because it doubles as an accumulator.
Accumulators
These are plants that “mine” nutrients from deep in the soil and bring the to the surface where other plants will be able to access them. Good examples include alfalfa, comfrey, borage, and chicory. For more ideas look at deep rooted perennial plants. For my peach tree guild I would opt for chicory as it offers medicinal benefits for both humans and livestock.
Once you’ve got all your plants you can begin planting. Obviously it’s easiest to start with the tree and work your way out. You should consider how much space it will need and shade it will create as it grows when selecting locations for other perennials.
Utilizing this permaculture method can help you make the most out of your orchard space by incorporating other edible, medicinal, or flowering crops into your design and keeping your trees healthy and productive. It can also make your space more habitable for beneficial wildlife like birds, pollinators, and beneficial insects which lose habitat when space between trees is mowed. Lastly it may even help reduce erosion when compared to traditional orchard set ups. What’s there to lose?
Pin it for later.